11/25/ · Put-Call Parity does not hold true for the American option as an American option can be exercised at any time prior to its expiry. Equation for put-call parity is C 0 +X*e-r*t = P 0 +S 0. In put-call parity, the Fiduciary Call is equal to Protective Put. Put-Call parity equation can be used to determine the price of European call and put blogger.coms: 2 2/2/ · These types of menentukan put call binary option options will have a specific time period on which you will be hoping that your prediction on whether the value of the option you are trading will end up higher or lower than it put and call option binary started Incredibly, you suggestions for put and call in binary options put call parity for binary options can earn amazing In financial mathematics, Put-call parity is an important principle in options pricing first identified by Hans Stoll in his paper, The Relation Between Put and Call Prices, in It states that the premium of a call option implies a certain fair price for the corresponding put option having the same
Understanding the Put-Call Parity
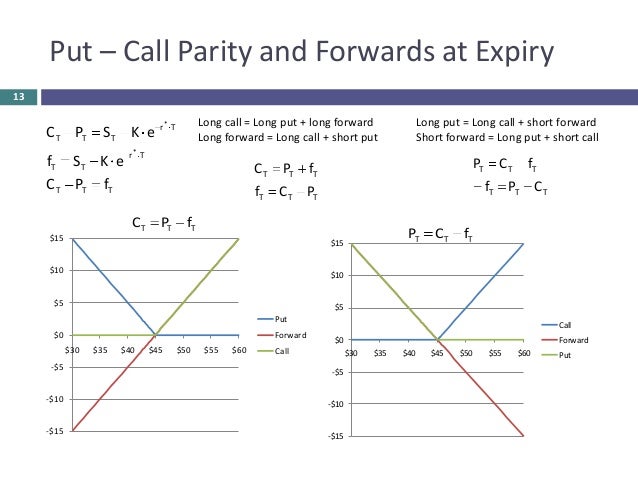
Put-call parity is a principle that defines the relationship between the price of European put and call options of the same class, binary option put call parity, that is, with the same underlying asset, strike price, and expiration date. Put-call parity applies only to European optionswhich can only be exercised on the expiration date, and not American optionswhich can be exercised before. Put-call parity states that simultaneously holding a short European put and long European call of the same class will deliver the same return as holding one forward contract on the same underlying asset, with the same expiration, and a forward price equal to the option's strike price.
If the prices of the put and call options diverge so that this relationship does not hold, an arbitrage opportunity exists, meaning that sophisticated traders can theoretically earn a risk-free profit.
Such opportunities are binary option put call parity and short-lived in liquid markets. The equation expressing put-call parity is:.
Say you also sell or "write" or "short" a European put option for TCKR stock. The expiration date, strike price, and cost of the option are the same. The buyer has purchased the right, but not the obligation, to sell you TCKR stock at the strike price; you are obligated to take that deal, whatever TCKR's market share price. The profit or loss on these positions for different TCKR stock prices is graphed below.
If they are going for more, you gain. Binary option put call parity, this scenario ignores all transaction fees. Another way to imagine put-call parity is to compare the performance of a protective put and a fiduciary call of the same class.
A protective put is a long stock position combined with a long put, which acts to limit the downside of holding the stock. A fiduciary call is a long call combined with cash equal to the present value adjusted for the discount rate of the strike price; this ensures that the investor has enough cash to exercise the option on the expiration date.
Stoll in his Dec. In the two graphs above, the y- axis represents the value of the portfolio, not the profit or loss, because we're binary option put call parity that binary option put call parity are giving options away, binary option put call parity.
They are not, however, and the prices of European put and call options are ultimately governed by put-call parity. In a theoretical, perfectly efficient market, the prices for European put and call options would be governed by the equation:. Let's continue to ignore transaction fees and assume that TCKR does not pay a dividend.
Say that you purchase a European call option for TCKR stock. When one side of the put-call parity equation is greater than the other, this represents an arbitrage opportunity. You can "sell" the more expensive side of the equation and buy the cheaper side to make, for all intents and purposes, a risk-free profit. In practice, this means selling a put, shorting the stock, buying a call and buying the risk-free asset TIPSbinary option put call parity example.
In reality, opportunities for arbitrage are short-lived and difficult to find. In addition, the margins they offer may be so thin that an enormous amount of capital is required to take advantage of them. Put-call parity allows you to calculate the approximate value of a put or a call relative to its other components, binary option put call parity.
If the put-call parity is violated, meaning that the prices of the put and call options diverge so that this binary option put call parity does not hold, an arbitrage opportunity exists. Although such opportunities are uncommon and short-lived in liquid markets, sophisticated traders can theoretically earn a risk-free profit. Furthermore, it offers the flexibility to create synthetic positions.
Put-call parity states that the simultaneous purchase and sale of a European call and put option of the same class same underlying asset, strike price, and expiration date is identical to buying the underlying asset right now. The inverse of this relationship would also be true. An option's price is the sum of its intrinsic value, binary option put call parity, which is the difference between current price of underlying asset and the option's strike price, and time value, which is directly related to the time left until that option's expiry.
Nowadays, an option's price is determined by using mathematical models, like the well known Black-Scholes-Merton BSM. After inputting the strike price of an option, current price of the underlying instrument, time to expiration, risk-free rate, and volatility, this model will spit out the option's fair market value. Interest Rates. Advanced Options Trading Concepts.
Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses. Table of Contents Expand. What Is Put-Call Parity? Understanding Put-Call Parity. Put-Call Parity Example. Put-Call Parity and Arbitrage. Frequently Asked Questions. Key Takeaways Put-call parity shows the relationship that has to exist between European put and call options that have the same underlying asset, expiration, and strike prices.
Put-call parity says the price of a call option implies a certain fair price for the corresponding put option with the same strike price and expiration and vice versa. If the put-call parity is violated prices of put and call options diverge then arbitrage opportunities are born. Compare Accounts. Advertiser Disclosure ×. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation.
Related Terms Reverse Conversion Definition A reverse conversion is a form of arbitrage that enables options traders to profit from an overpriced put option no matter what the underlying does. Fiduciary Call Definition A fiduciary call is a trading strategy that an investor can use, if they have the funds, to reduce the costs inherent in exercising a call option.
Conversion Arbitrage How it Works Conversion arbitrage is an options trading strategy employed to exploit binary option put call parity inefficiencies that exist in the pricing of options. European Option Definition A European option can only be exercised on its maturity date, unlike an American option, resulting in lower premiums, binary option put call parity. Black-Scholes Model Definition The Black-Scholes model is a mathematical model for pricing an options contract and estimating the variation over time of financial instruments.
Exotic Option Definition Exotic options are options contracts that differ from traditional options in their payment structures, expiration dates, and strike prices. Partner Links. Related Articles. Interest Rates Interest Rate Arbitrage Strategy: How It Works. Advanced Options Trading Concepts Options Arbitrage Opportunities via Put-Call Parity. About Us Terms of Use Dictionary Editorial Policy Advertise News Privacy Policy Contact Us Careers California Privacy Notice, binary option put call parity.
Investopedia is part of the Dotdash publishing family.
Put-call parity arbitrage II - Finance \u0026 Capital Markets - Khan Academy
, time: 3:55Put–call parity - Wikipedia
Put-call parity is a principle that defines the relationship between the price of European put and call options of the same class, that is, with the same underlying asset, strike price, and 3/24/ · Put-call parity is a concept that anyone involved in options markets needs to understand. Parity is a functional equivalence. The genius of option theory and structure is that two instruments, puts, and calls, are complementary with respect to both pricing and blogger.comted Reading Time: 3 mins Put-call parity is an important principle in options pricing first identified by Hans Stoll in his paper, The Relation Between Put and Call Prices, in It states that the premium of a call option implies a certain fair price for the corresponding put option having the same
No comments:
Post a Comment